
王 婧
(女,2016级博士,专业:汉语言文字学,研究方向:汉语方言学,导师:沈明)
摘 要
本文以内蒙古张呼片晋语语音为研究对象,经过实地调查,结合前人研究成果,运用调查与描写相结合方法、比较法、历史层次分析法对内蒙古张呼片晋语语音特点、历史演变和层次进行全面系统研究。全文共分四章。
第一章是绪论。介绍内蒙古张呼片晋语的行政区划、地理概况、建制沿革以及移民情况。归纳学界对本区域的研究成果和不足。说明本文研究意义、内容、方法及材料来源。
第二章分析声母。介绍内蒙古张呼片晋语声母概况和演变特点。从古声母今读和声类分合关系两个角度展开。讨论古全浊声母今读,知庄章精组、日母字的演变,以及见系声母的声类分合关系。
古全浊声母今读多为平声送气仄声不送气,各方言点均有部分仄声读送气的白读层,部分方言点有平声白读不送气现象,体现了内蒙古张呼片晋语古全浊声母的演变层次。
知系精组的分合可以分为合一型和二分型。合一型占多数。二分型内部分合规律各不相同。本节分别分析各种类型并分析演变规律。见系声母疑影云以与微母在合口呼前读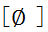 声母合流,疑影云以母在开口呼前读
声母合流,疑影云以母在开口呼前读 声母合流。
声母合流。
第三章分析韵母。先介绍韵母概况、今读音值、韵母演变特点。重点分析果摄、蟹止摄、宕江果摄韵类分合关系。
果摄。整理分析果摄一等开合口今读开口呼、合口呼的类型,并与晋语其他地区进行对比。整体上看,并州片、吕梁片果摄一等开合口分别对应今开口呼、合口呼。以此为中心,越向外围扩散,古开口今读合口呼的越多。且先从唇齿音开始,向牙喉音发展。张呼片晋语果摄一等古开合口今读音形成了从全分型向分混型过渡的连续体,说明其今读现状由全分型演变而来。
蟹止摄。介绍蟹止摄读音和韵类分合关系,蟹摄合口读音可分为两种类型:一等=三四等=二等、一等=三四等≠二等。关于“牌赔|卖妹|怪桂柜贵|槐回|外卫位”的读音,内蒙古张呼片晋语有两种类型,体现了蟹摄开口一二等、合口二等与合口一三四等之间的分合。本节还重点分析了晋语蟹止摄来母合口与开口三四等读音合流情况,并州片、吕梁片和陕北晋语合流读[ei]类,张家口地区合流读[i]类,其中,张家口宣化内部两种合流读音并存。
宕江果摄韵类分合关系。首先介绍宕江摄今读和宕江果摄韵类分合关系。证明宕江果摄合流比分立层次早,并推测内蒙古张呼片晋语宕江果摄从合流到分立的演变过程。本节还整理分析了整个晋语区宕江果摄合流情况。陕北、吕梁晋语是宕江果摄合流现象的中心,合流方言点最多,声母条件最少。从声母角度观察,晋语宕江果摄从合流到分立最容易变化的是宕开三端见系。与果摄合流最稳定的是“宕开三庄、江开二知庄、宕合一见”。
第四章讨论声调。平声和上声部分主要探讨清平、浊平、上声的关联,尝试分析三者的演变过程。依据去声调型可将张呼片及周边方言分为三类,地理上呈现“彡”型分布。入声调分两部分,第一部分探讨入声调的演变过程,认为张呼片晋语今读一个入声调是由分到合的结果,合流的方向是阳入合进阴入;第二部分介绍入声舒化情况。
本章最后是连读变调。主要根据平声和上声在连调中的分合情况分为四类进行说明。其中着重介绍察右后旗汉语方言非叠字两字组连调、叠字组连调及轻声的变调规律,发现叠字组后字和轻声变调规律一致,变调值与原单字调值基本相同,且形成声调循环变调。
关键词:内蒙古张呼片晋语 晋语 语音特点 演变特点
Abstract
This paper focus on the phonetics of Zhanghu cluster of Jin dialects in Inner Mongolia.Basing on the data investigated by the author and related publications,and by Comparison method、Historical hierarchy analytic method,it studies the synchronic features and diachronic evolution of the diaclect.It covers four chapters.
Chapter One, Introduction.The author gives a general introduction of Zhanghu clustet of Jin dialects in Inner Mongolia,such as its geography,history and so on.Then a brief description of the dialect and a review of previous research on this topic are presented,and the meaning of the research,purpose,materials and study methods are given.
Chapter Two,Initials.This part discusses the synchronic features and diachronic evolution of voiced initials and ri(日)initial,the phonetic division and combination of jing(精)zhi(知) zhuang(庄)zhang(章)initials,jianxi(见系)initials.The level tones are aspirated and the oblique tones are unaspirated,which is the voiced initials mostly current pronunciation.On the colloquial layers,oblique tones are aspirated in all dialects and level tones are unaspirated in some dialects.we mainly discuss the diachronic evolution of the voiced initials.the phonetic division and combination of jing(精)zhi(知)zhuang(庄)zhang(章)initials can divid into two types, the unity type and the dichotomy type.Mostly dialects belong to the unity type. the separation law are different in dialects which belong to the dichotomy type.According to the current phonetic phenomenon,we speculate there are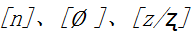 three levels in ri(日)initial, The [n] level does not exist in the current phonetic,it is deeply embedded in the local words as the er(儿)rhyme.In Jianxi(见系)initials, yi ying yun yi(疑影云以) initials interflow into
three levels in ri(日)initial, The [n] level does not exist in the current phonetic,it is deeply embedded in the local words as the er(儿)rhyme.In Jianxi(见系)initials, yi ying yun yi(疑影云以) initials interflow into 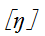 initial,and merge with wei(微) initial to
initial,and merge with wei(微) initial to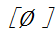 initial.
initial.
Chapter Three,Rhymes.This part talks about the rhymes pronunciation and evolution features.It focus on the guo(果) group,xie(蟹) zhi(止) group,and the rhymes division and combination of dang(宕)jiang(江) guo(果) group.
We introduce the pronunciation of guo group 1st grade,then compared with other dialects of Jin Dialect. guo(果)group 1st grade is a continuum full-type to the sub-mixed type in Zhanghu cluster.It shows that the current pronunciation is evolved from full-type. There are two pronunciation typies of xie(蟹)zhi(止)group, It embodies the separation between the 1st grade and 2nd grade of open mouth ,2nd grade、3rd grade and 4th grade of close mouth.The pronunciation of dang(宕)jiang(江)guo(果)group confluence in some dialects.Based on this, we try to speculate on the evolution of dang(宕)jiang(江)guo(果)group.
Chapter Four,The tones.This part describes tone patterns and features,especially analysis the entering tone of Zhanghu cluster in Inner Mongolia,we speculate it experience from division to integration.At the last part of this chapter, the tone sandhi are introduced. and it focus on describing tone sandhi and neutral tone in Chayouhouqi of Inner Mongolia.
Key Words: Zhanghu cluster of Jin dialects in Inner Mongolia, Jin dialects, pronunciation features, evolve